Gastrointestinal (GI) cancer is a term used for the group of cancers that affect the gastrointestinal tract and other organs that are contained within the digestive system, including the esophagus, pancreas, stomach, colon, rectum, anus, liver, biliary system, and small intestine.
GI Malignancy is also known as GI (Gastrointestinal) Cancer. It is a malignant or cancerous condition of the gastrointestinal tract (GI tract). GI cancer mainly affects the organs of digestive system. Human digestive system includes various organs such as esophagus, stomach, biliary system, pancreas, small intestine, large intestine, rectum and anus. GI Malignancy includes cancers of the Oesophagus, Gallbladder, Biliary Tract, Liver, Pancreas, Stomach, Small Intestine, Bowel (Large Intestine or Colon and Rectum) and Anus. GI cancer can occur in any men and women. Gastrointestinal Cancer Doctor In Vashi,Navi Mumbai.
Colorectal cancer
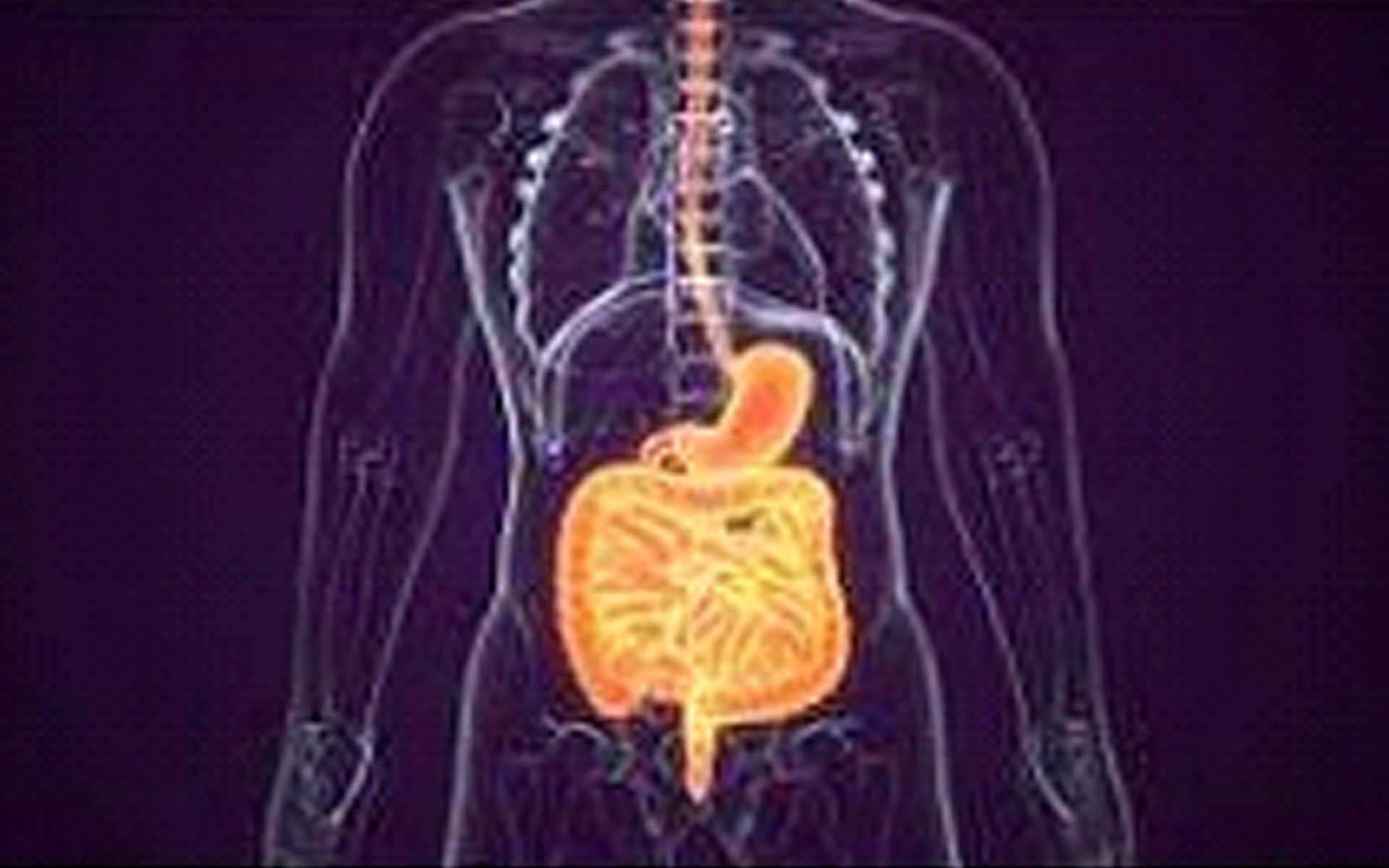
Colorectal cancer is cancer that occurs in the colon or rectum. Sometimes it is called colon cancer, for short. As the drawing shows, the colon is the large intestine or large bowel. The rectum is the passageway that connects the colon to the anus.
Sometimes abnormal growths, called polyps, form in the colon or rectum. Over time, some polyps may turn into cancer. Screening tests can find polyps so they can be removed before turning into cancer. Screening also helps find colorectal cancer at an early stage, when treatment works best.
If you have symptoms, they may include :
● A change in bowel habits.● Blood in or on your stool (bowel movement).
● Diarrhea, constipation, or feeling that the bowel does not empty all the way.
● Abdominal pain, aches, or cramps that don’t go away.
● Losing weight and you don’t know why.
Your risk of getting colorectal cancer increases as you get older. Other risk factors include having :
● Inflammatory bowel disease such as Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis.● A personal or family history of colorectal cancer or colorectal polyps.
● A genetic syndrome such as familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) or hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer (Lynch syndrome).
Lifestyle factors that may contribute to an increased risk of colorectal cancer include :
● Lack of regular physical activity.● A diet low in fruit and vegetables.
● A low-fiber and high-fat diet, or a diet high in processed meats.
● Overweight and obesity.
● Alcohol consumption.
● Tobacco use.
Liver Cancer

In its early stages, liver cancer may not have symptoms that can be seen or felt. However, as the cancer grows larger, people may notice one or more of these common symptoms. It’s important to remember that these symptoms could also be caused by other health conditions. If you have any of these symptoms, talk to your doctor.
Liver cancer symptoms may include :
● Discomfort in the upper abdomen on the right side.● A swollen abdomen.
● A hard lump on the right side just below the rib cage.
● Pain near the right shoulder blade or in the back.
● Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes).
● Easy bruising or bleeding.
● Unusual tiredness.
● Nausea and vomiting.
● Loss of appetite.
● Weight loss for no known reason.
Behaviors and conditions that increase risk for getting liver cancer are :
● Being overweight or having obesity.● Having a long-term hepatitis B virus or hepatitis C virus infection.
● Smoking cigarettes.
● Drinking alcohol.
● Having cirrhosis (scarring of the liver, which can also be caused by hepatitis and alcohol use).
● Having nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (extra fat in the liver that is not caused by alcohol).
● Having diabetes or non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
You can lower your risk of getting liver cancer in the following ways :
● Keep a healthy weight.● Get vaccinated against Hepatitis B. The Hepatitis B vaccine is recommended for all infants at birth and for adults who may be at increased risk.
● Get tested for Hepatitis C, and get medical care if you have it.
● Don’t smoke, or quit if you do.
● Avoid drinking too much alcohol. Gastrointestinal Cancer Doctor In Vashi,Navi Mumbai.
