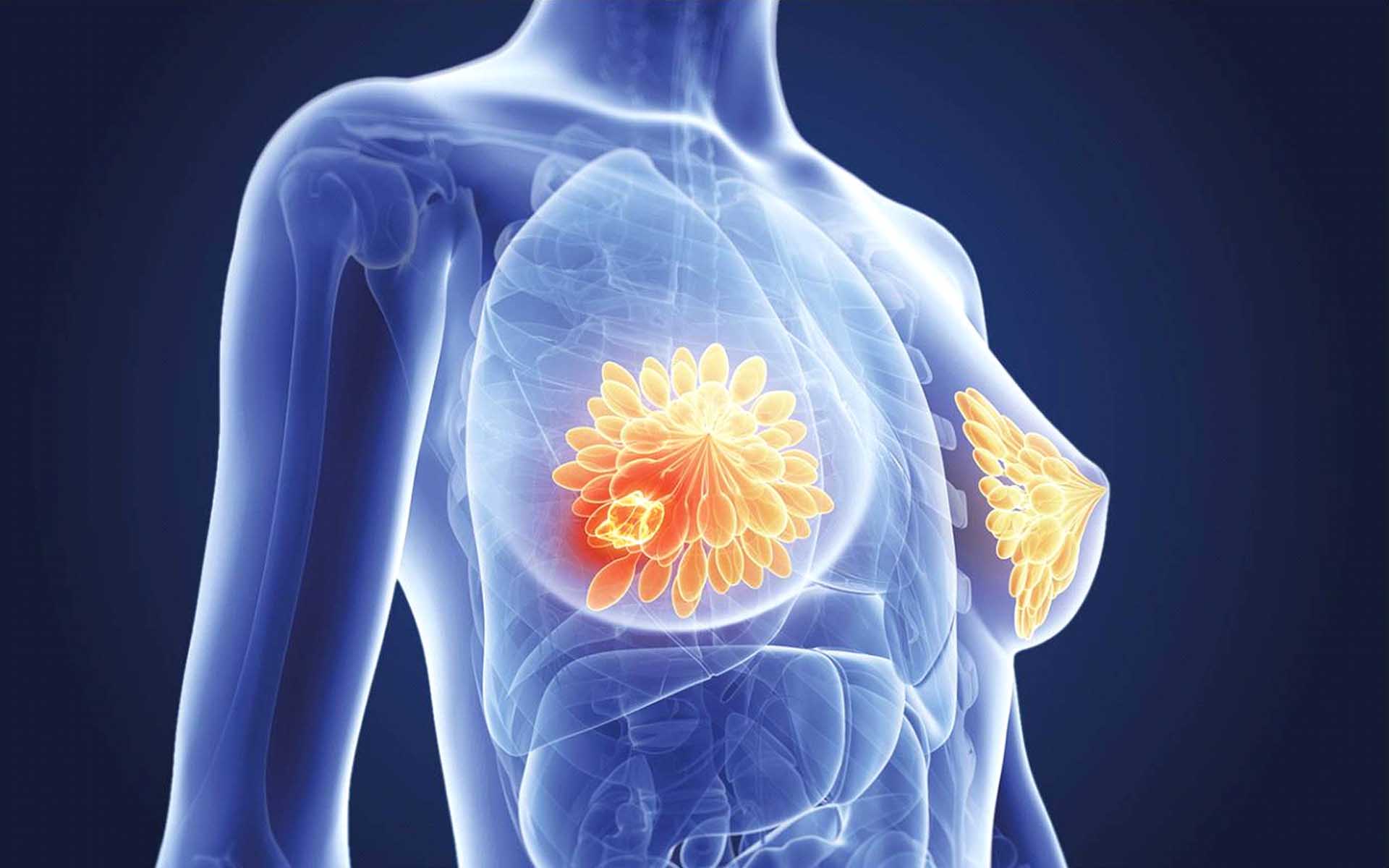
Breast cancer is a disease in which cells in the breast grow out of control. There are different kinds of breast cancer. The kind of breast cancer depends on which cells in the breast turn into cancer.
Breast cancer can begin in different parts of the breast. A breast is made up of three main parts: lobules, ducts, and connective tissue. The lobules are the glands that produce milk. The ducts are tubes that carry milk to the nipple. The connective tissue (which consists of fibrous and fatty tissue) surrounds and holds everything together. Most breast cancers begin in the ducts or lobules.
The most common kinds of breast cancer are :
● Invasive ductal carcinoma : The cancer cells grow outside the ducts into other parts of the breast tissue. Invasive cancer cells can also spread, or metastasize, to other parts of the body.● Invasive lobular carcinoma : . Cancer cells spread from the lobules to the breast tissues that are close by. These invasive cancer cells can also spread to other parts of the body.
Risk Factors You Cannot Change :
● Getting older : The risk for breast cancer increases with age; most breast cancers are diagnosed after age 50.● Genetic mutations : . Inherited changes (mutations) to certain genes, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2. Women who have inherited these genetic changes are at higher risk of breast and ovarian cancer.
● Reproductive history : Early menstrual periods before age 12 and starting menopause after age 55 expose women to hormones longer, raising their risk of getting breast cancer.
● Having dense breasts : Dense breasts have more connective tissue than fatty tissue, which can sometimes make it hard to see tumors on a mammogram. Women with dense breasts are more likely to get breast cancer.
● Personal history of breast cancer or certain non-cancerous breast diseases : Women who have had breast cancer are more likely to get breast cancer a second time. Some non-cancerous breast diseases such as atypical hyperplasia or lobular carcinoma in situ are associated with a higher risk of getting breast cancer.
● Family history of breast or ovarian cancer : A woman’s risk for breast cancer is higher if she has a mother, sister, or daughter (first-degree relative) or multiple family members on either her mother’s or father’s side of the family who have had breast or ovarian cancer. Having a first-degree male relative with breast cancer also raises a woman’s risk.
Risk Factors You Can Change :
● Not being physically active : Women who are not physically active have a higher risk of getting breast cancer.● Being overweight or obese after menopause : Older women who are overweight or obese have a higher risk of getting breast cancer than those at a normal weight.
● Taking hormones : Some forms of hormone replacement therapy (those that include both estrogen and progesterone) taken during menopause can raise risk for breast cancer when taken for more than five years. Certain oral contraceptives (birth control pills) also have been found to raise breast cancer risk.
● Reproductive history : Having the first pregnancy after age 30, not breastfeeding, and never having a full-term pregnancy can raise breast cancer risk.
● Drinking alcohol : Studies show that a woman’s risk for breast cancer increases with the more alcohol she drinks.
Breast cancer is treated in several ways. It depends on the kind of breast cancer and how far it has spread. People with breast cancer often get more than one kind of treatment.
● Surgery : An operation where doctors cut out cancer tissue.● Chemotherapy : Using special medicines to shrink or kill the cancer cells. The drugs can be pills you take or medicines given in your veins, or sometimes both.
● Hormonal therapy : Blocks cancer cells from getting the hormones they need to grow.
● Biological therapy : Works with your body’s immune system to help it fight cancer cells or to control side effects from other cancer treatments.
● Radiation therapy : Using high-energy rays (similar to X-rays) to kill the cancer cells.
